Risk Assessment
Comprehensive pre-production security and risk analysis for AI agents. Understand security hazards, operational risks, and compliance gaps before deployment.
Overview
Agent Inspector provides multi-dimensional risk assessment that goes beyond traditional application security. Because AI agents are non-deterministic and make autonomous decisions, they require a new approach to security and risk management.
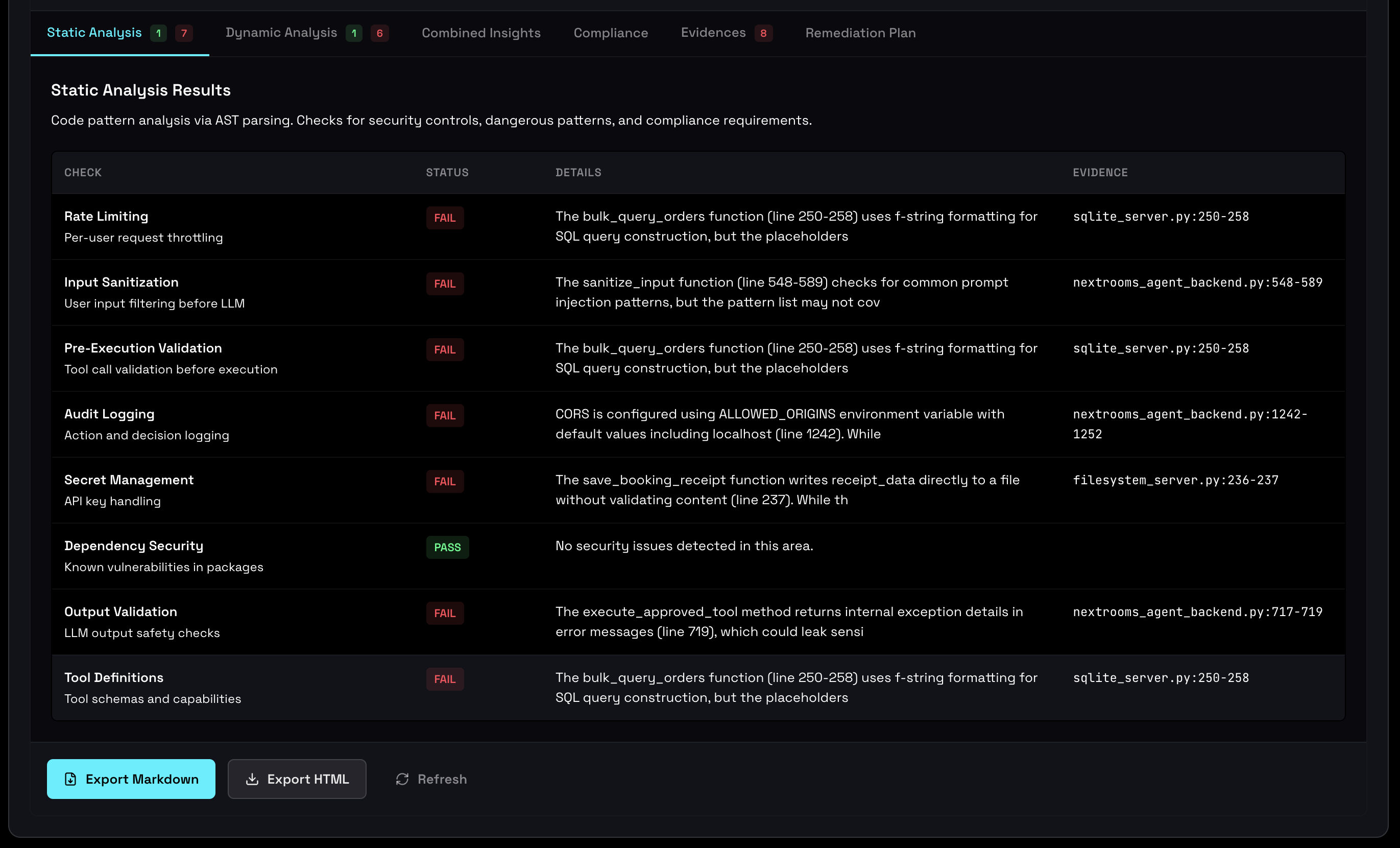
The risk assessment capability automatically analyzes your agent across five critical dimensions, identifying security hazards, compliance gaps, and operational risks before they reach production.
Security and Behavioral Assessment
Agent Inspector performs comprehensive security analysis that identifies both traditional security vulnerabilities and behavioral risks unique to AI agents. This assessment includes checks across resource management, behavioral stability, environment configuration, and privacy compliance.
Each finding is categorized by severity with specific remediation guidance:
- Critical (shown as FAIL): Security hazards that must be addressed before production
- Warning (shown as WARN): Issues that may cause problems but don't block deployment
- Info: Recommendations for optimization and best practices
Comprehensive security assessment showing hazards by severity and behavioral metrics
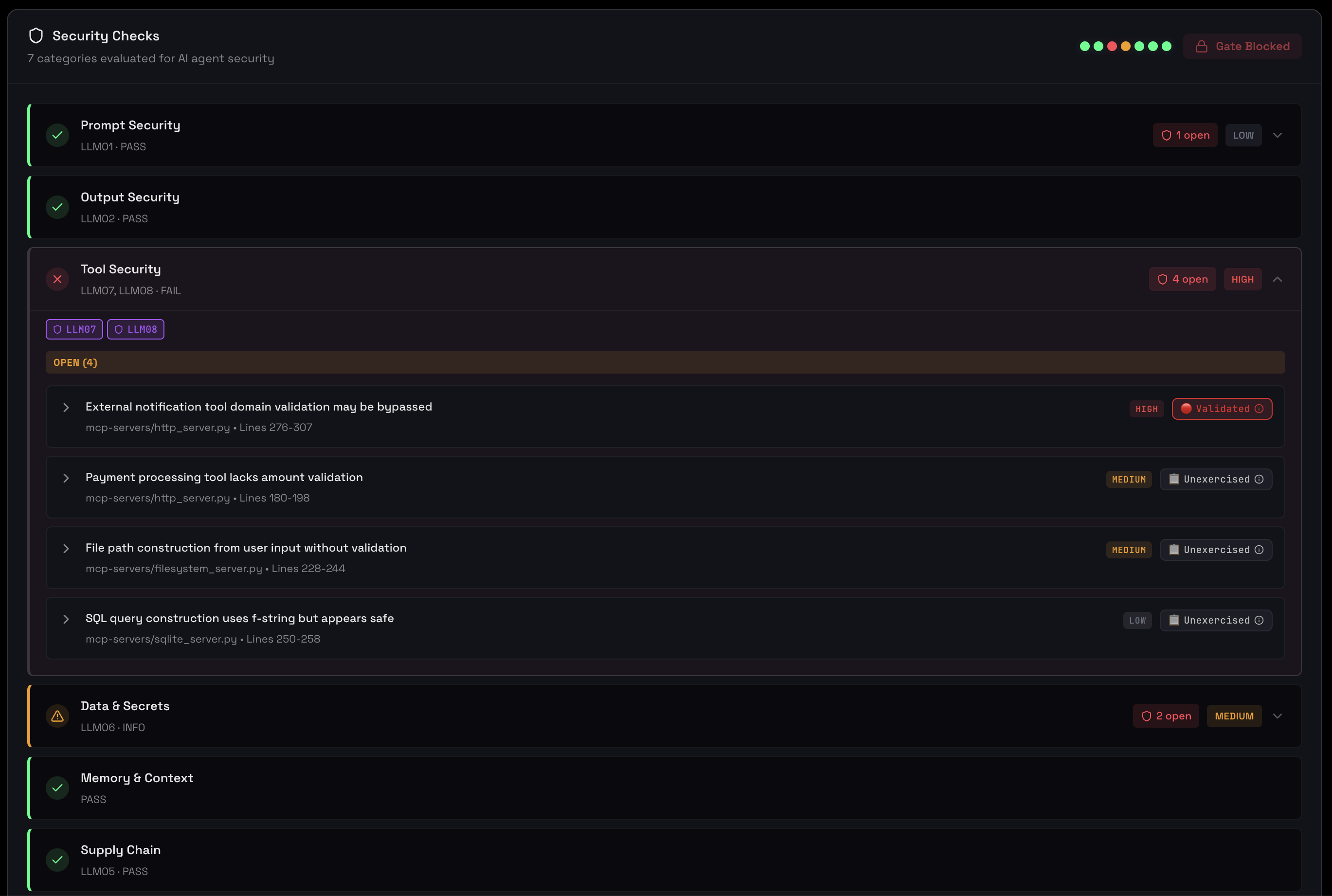
Environment & Supply Chain
Track which LLM models your agent uses, whether they're pinned to specific versions, and the security posture of your tool dependencies. Supply chain visibility is critical for production readiness and compliance.
Model version tracking, tool adoption rates, and supply chain consistency
Key Insights
- Model Pinning: Identifies unpinned model versions that could introduce unexpected behavior changes
- Tool Adoption: Shows which tools are actively used vs. configured but unused
- Version Consistency: Detects version drift across different agent sessions
- Dependency Health: Tracks third-party integrations and their usage patterns
Unpinned models (e.g., "claude-3-5-sonnet-latest") can change behavior without warning when providers update their models. In production, this creates unpredictable behavioral drift. Always pin to specific versions (e.g., "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022") for stability.
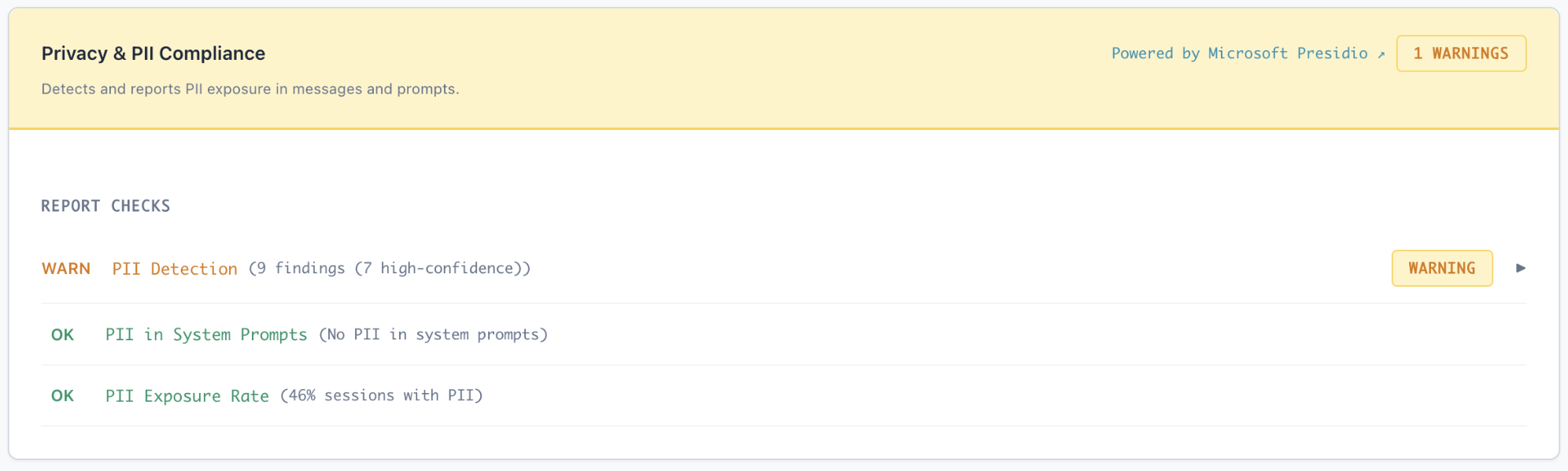
Privacy & PII Detection
Agent Inspector automatically scans all prompts, tool calls, and responses for sensitive information using Microsoft Presidio. This helps you identify privacy risks before they become compliance violations.
Privacy & PII Compliance report showing detection findings and exposure rates
Detected Entity Types
Personal Identifiers
Names, email addresses, phone numbers, and social security numbers
Financial Data
Credit card numbers, bank accounts, and payment information
Location Information
Addresses, GPS coordinates, and location-based data
Health Information
Medical record numbers and health-related personal data
Understanding PII Exposure
The dashboard shows:
- Exposure Rate: Percentage of sessions that contain PII
- Entity Breakdown: Distribution of PII types detected
- Location Context: Where PII appears (prompts, responses, tool calls)
- Specific Examples: Actual detected values for validation and remediation
PII exposure in agent interactions can violate GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and other privacy regulations. Use this data to implement proper data masking, tokenization, or access controls before production deployment.
Resource Management
Understand how your agent consumes resources across sessions. Resource management analysis helps prevent cost overruns, performance issues, and runaway executions in production.
Token usage, execution time, and tool call metrics across sessions
Resource Metrics
Token Usage
- Average tokens per session
- Input vs. output distribution
- Token spikes and outliers
- Cost projection
Execution Time
- Average session duration
- Latency patterns
- Slow sessions identification
- Performance trends
Tool Calls
- Calls per session
- Tool call sequences
- Inefficient patterns
- Unused tools
Resource Bounds
Agent Inspector checks whether your agent has appropriate resource bounds configured:
- Max Tokens: Ensures token limits are set to prevent runaway costs
- Timeout Controls: Verifies execution time limits are in place
- Iteration Limits: Checks for controls on multi-turn interactions
- Rate Limiting: Identifies missing rate limit protections
Production Readiness Gates
Five mandatory gates that combine security, behavioral, and operational criteria into a clear go/no-go decision for production deployment. Each gate must pass before your agent is considered production-ready.

Production gates showing pass/fail status with specific remediation guidance
The Five Gates
Gate 1: Behavioral Stability
Criterion: Stability Score ≥ 80%
Ensures your agent behaves consistently across sessions. Low stability indicates unpredictable behavior that could cause production issues.
Gate 2: Security Assessment
Criterion: No CRITICAL or HIGH security hazards (or VALIDATED findings)
All critical security findings must be resolved or dismissed with justification. VALIDATED findings from correlation have higher priority.
Gate 3: Supply Chain Integrity
Criterion: Model versions pinned, tools validated
Models must be pinned to specific versions, and all tools must have documented purposes and security posture.
Gate 4: Resource Bounds
Criterion: Token limits, timeouts, and rate limits configured
Prevents runaway costs and resource exhaustion with proper constraints on execution.
Gate 5: Audit & Compliance
Criterion: Critical actions logged, PII handling documented
Ensures compliance requirements are met with proper audit trails and data handling procedures.
Production gates are designed to integrate with your deployment pipeline. Fail the build if gates don't pass, forcing teams to address issues before production deployment. This creates a safety net that catches problems early.
How to Use Risk Assessment
1. Run Sufficient Test Volume
Risk assessment accuracy improves with more data. Different confidence levels require different amounts of data:
- 20 sessions: Minimum for basic behavioral clustering
- 30-50 sessions: Ideal for reliable analysis with medium confidence
- 100+ sessions: Best for complex agents, provides high confidence
- 200+ sessions: Required for meaningful outlier rate evaluation
Run tests with diverse inputs to capture the full range of agent behavior and potential risks.
2. Test Edge Cases
Include scenarios that stress-test your agent's boundaries:
- Malformed or unexpected inputs
- Permission edge cases and access control tests
- Resource-intensive operations
- Error conditions and recovery scenarios
- Concurrent or rapid-fire requests
3. Review All Findings
Don't just check the pass/fail status. Review each finding in detail:
- Understand root causes of security hazards
- Validate PII detections (false positives can occur)
- Analyze resource usage patterns for optimization
- Document acceptance of warnings and risks
4. Iterate and Re-Test
After addressing findings, run the assessment again to verify fixes:
- Confirm critical hazards are resolved
- Validate that changes didn't introduce new risks
- Ensure behavioral stability improved or remained stable
- Verify production gates now pass
5. Generate Reports for Stakeholders
Use the dashboard to create evidence for security reviews and production approvals. The quantitative metrics and specific findings give security teams the data they need to make informed decisions.
Best Practices
Run Early and Often
Don't wait until pre-production. Run risk assessment during development to catch issues when they're cheap to fix.
Integrate with CI/CD
Make risk assessment part of your automated pipeline. Block deployments that fail production gates.
Track Over Time
Compare assessments across versions to ensure changes improve rather than degrade security posture.
Document Decisions
For warnings you choose to accept, document the reasoning and any mitigating controls you've implemented.