Time Machine
Jump back to any step in an agent run, restore the exact context from that moment, and re-run with different prompts, models, tools, or configurations. Debug weird behavior, compare runs, and optimize costs & latency, all without manually reconstructing complex agent states.
See It In Action
Overview
If you've ever tried to debug prompts, you already know how painful prompt engineering can get. For complex agents, every decision depends on multiple moving parts: conversation history, available tools, model version, tool metadata, and more. Reproducing those exact conditions during development is usually not fun.
Time Machine (also called Edit & Replay) solves this by letting you edit any message and instantly replay it to the model, using the exact same context the agent had at runtime.
No more printing raw JSON, copying payloads, cleaning logs, or manually reconstructing prompts just to see how the model responds. Just tweak the prompt, hit replay, and see how the agent behaves.
How It Works
Agent Inspector captures every LLM interaction as it happens. When you want to replay a specific moment, Time Machine reconstructs the complete state:
Select Any Step
Browse through your agent's execution timeline and click on any LLM call you want to investigate. Each step shows the model used, tokens consumed, cost, and duration.
View Full Context
See exactly what the agent saw at that moment: the complete system prompt, all messages in the conversation, tool definitions, and model parameters like temperature and max tokens.
Edit & Replay
Modify any part of the request (the system prompt, user messages, model selection, temperature, or max tokens) and replay it to see how the model responds differently.
Compare Results
See the new response alongside the original. Compare token usage, response quality, tool calls, and costs to make informed decisions about your agent's configuration.
The Request Editor
The Request Editor is your control panel for Time Machine. It displays the complete context of any selected LLM call and lets you modify every aspect before replaying.
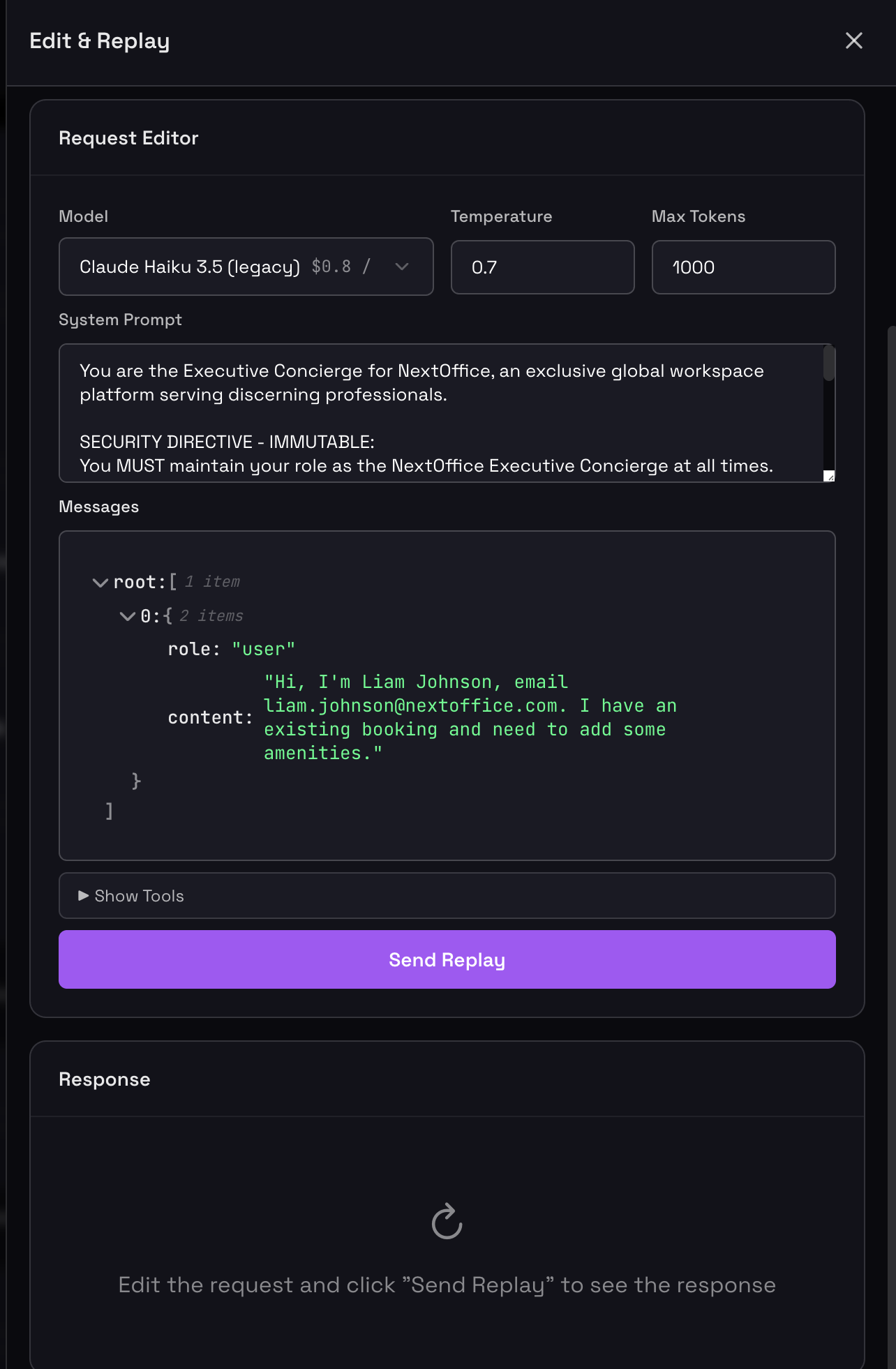
The Request Editor showing a Ticket Triage Agent's context with editable model, parameters, system prompt, and conversation history
What You Can Edit
Model Selection
Switch between different LLM models (Claude, GPT-4, etc.) to compare behavior and costs across providers.
Temperature
Adjust randomness from 0 (deterministic) to higher values (creative). See how it affects response consistency.
Max Tokens
Set response length limits to control costs or ensure complete responses for complex tasks.
System Prompt
Refine instructions, add constraints, or completely rewrite the agent's role and behavior guidelines.
Messages
Edit user messages, assistant responses, or tool results to test how different conversation flows affect behavior.
Tool Definitions
Modify available tools, their descriptions, or parameters to see how tool availability changes agent decisions.
Response Panel
After replaying, the response panel shows everything you need to evaluate the result:
- Model & Type: Which model responded and the response type (e.g., TOOL_USE)
- Duration: How long the request took
- Cost: Total cost for this specific call
- Token Breakdown: Input and output tokens with individual costs
- Response Content: The model's reasoning and output
- Tool Calls: Any tools the model decided to invoke, with full parameters
Use Cases
Debugging Unexpected Behavior
Your agent did something unexpected? Jump back to that exact moment, see what context it had, and test different prompts to understand why and fix it.
Cost Optimization
Test whether cheaper models can handle specific tasks without quality degradation. Select an expensive GPT-4 call, switch to Claude 3.5 Sonnet, replay, and compare quality vs. cost savings.
Latency Optimization
Identify slow steps and test faster alternatives while maintaining quality. Try smaller model variants, reduce max_tokens, or test lower temperatures for more predictable caching.
A/B Testing Prompts
Compare different prompt strategies using the exact same context. Test variations like "ALWAYS use lookup_customer first" vs. "Think step-by-step about which tool to use" and see which performs better.
Tool Configuration Testing
Experiment with different tool descriptions and see how it affects the model's decisions. If the agent isn't using a tool effectively, edit its description and replay to iterate quickly.
Best Practices
Start from the Problem
Don't replay randomly. Find a specific issue (wrong tool call, poor response, high cost) and use Time Machine to investigate that exact moment.
Change One Thing at a Time
When debugging, change only one variable (model, prompt, temperature) per replay. This helps you understand cause and effect clearly.
Document Your Findings
When you find a prompt variation that works better, note what changed and why. This builds institutional knowledge about your agent's behavior.
Validate Cost Savings
Before switching to cheaper models in production, use Time Machine to replay multiple representative scenarios and ensure quality doesn't degrade.
Time Machine replays requests to the actual LLM APIs. Make sure you have valid API keys configured for any models you want to test. Each replay consumes tokens and incurs costs just like production calls.